
- #Putty ssh tunnel tcp port how to
- #Putty ssh tunnel tcp port install
- #Putty ssh tunnel tcp port free
- #Putty ssh tunnel tcp port windows
Copy the file MyFile.txt from your Linux user home directory to your Windows home directory by entering: C:\"Program Files (x86)"\PuTTY\pscp.exe.
Open a command prompt with Windows + R and enter cmd. You can use this to copy files to and from a Linux system. Look in the installation folder under C:\\Program Files (x86)\\PuTTY and find pscp.exe. In addition to the remote console, you can use PuTTY to transfer files via SSH.
#Putty ssh tunnel tcp port install
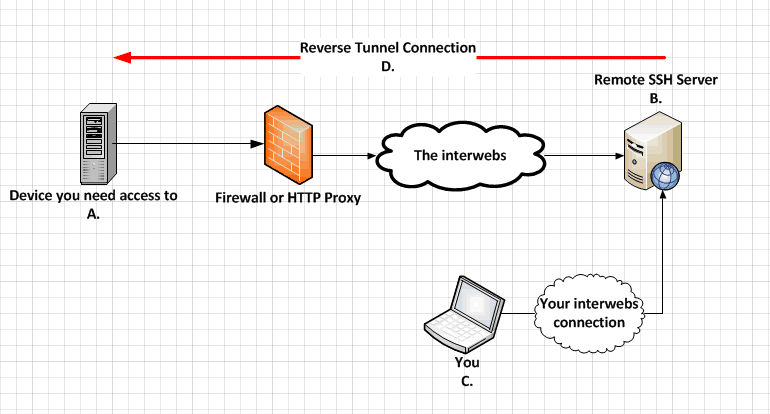
On Windows, download the PuTTY installer, then install and open it. └─577 /usr/sbin/sshd -D it's inactive, start it with the systemctl start sshd command. Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rvice enabled vendor preset: enabled)Īctive: active (running) since Fri 11:12:05 UTC 2 years 11 months ago Check whether the SSH daemon is already running by typing systemctl status sshd: $ systemctl status sshd The default configuration, where no line is uncommented, should work for this example. # OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where # The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with # This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin # This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. The configuration file is located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config and contains a lot of switches that can be activated by commenting out related lines: # $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.100 5 12:32:04 naddy Exp $ First, check the daemon's SSH configuration. The Linux system (Fedora 33 in my case) acts as the SSH server that allows the PuTTY SSH client to connect.
#Putty ssh tunnel tcp port how to
how to tunnel a certain protocol over SSH. how to copy files over the network, and 4. how to set up a remote console connection, 3. how to configure the SSH daemon on the Linux side, 2. In this article, I'll explain four ways to use SSH: 1. Because SSH traffic is encrypted, you can use SSH as a transport layer for any protocol that does not provide encryption by default. SSH can also be used to tunnel other network services. A common use case is the headless configuration of embedded devices, including the Raspberry Pi. You can use SSH to control almost any Linux machine, whether it's running as a virtual machine or as a physical device on your network. In Fedora 33, the SSH daemon is installed but not activated. You can hardly find a Linux distribution that does not come with the SSH daemon. The SSH server is usually running as a system daemon, so it is often called SSHD.
SSH uses a client-server architecture, where an SSH client establishes a connection to an SSH server.
#Putty ssh tunnel tcp port free
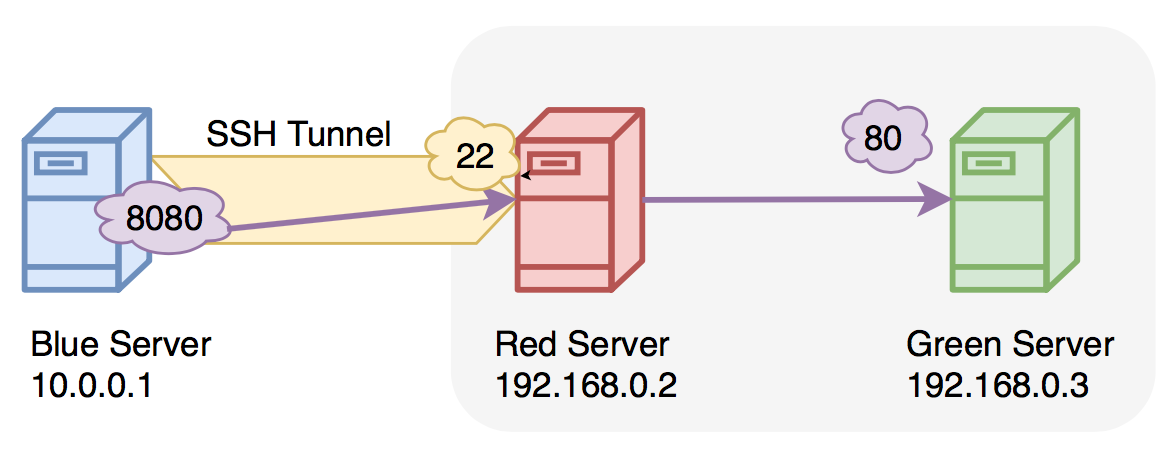
Free online course: RHEL Technical Overview.Thus it can replace the need for a VPN in a way. Using tunneling is good for security because the connection is encrypted and you don’t have to expose services to the outside. This will have the same effect as in the Putty. In the ssh console command simply specify ssh -L 8080:localhost:8080 when connecting to the remote host. With a Linux local box you can use simimlarly tunneling. Just open in your local browser and you will be connected to the remote server on TCP port 8080 via the SSH tunnel. Now you are ready to test your connection. If you need to connect to a different server through the remote host, you can specify it in place of localhost.ĭon’t forget to click on the Add button before establishing the connection. In the above example, the tunnel will be from the local TCP port 8080 to the remote TCP 8080 on localhost. Once you make sure tunneling is not forbidden, you can configure Putty by going to Tunnels tab in Putty’s configuration as seen below. The setting is called PermitTunnel and by default, in most configurations such as in CentOS, tunneling is allowed. You should know that SSH tunneling does not depend on the local OS and in this example I’ll use it with Windows and Putty.įirst, make sure tunneling is allowed on the remote server in the SSH daemon configuration. This can be easily done with SSH tunneling.
At the same time you wish to test the Tomcat and you need to connect to TCP 8080. The only connectivity you have to this remote host is SSH, i.e. Imagine, there’s a remote host which runs a Tomcat app servlet on TCP port 8080. Thus, to gain remote network access you can use a tunnel to a remote host which would act as an intermediary. SSH tunneling is very useful when the network access to a remote network is restricted.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
